Sciatica refers to pain that radiates along the path of the sciatic nerve, which branches from your lower back through your hips and buttocks and down each leg. Typically, sciatica affects only one side of your body.
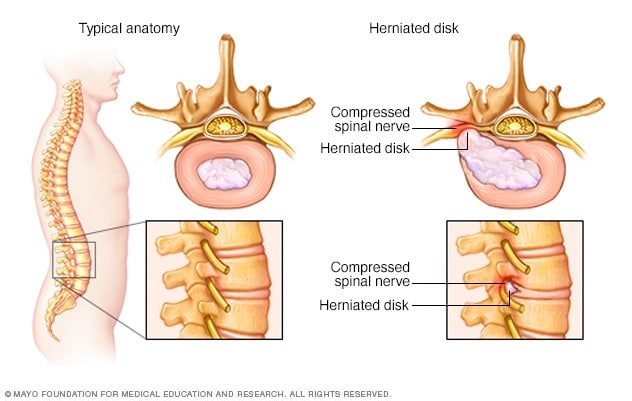
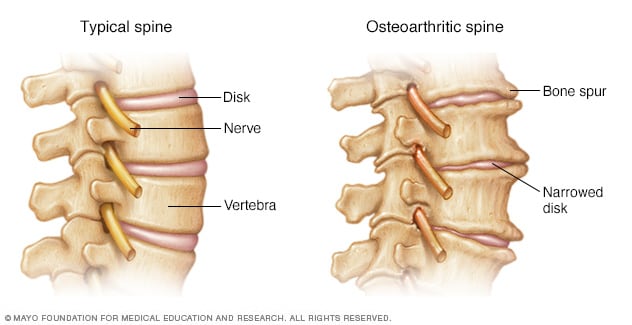
Sciatica most commonly occurs when a herniated disk, bone spur on the spine or narrowing of the spine (spinal stenosis) compresses part of the nerve. This causes inflammation, pain and often some numbness in the affected leg.
Although the pain associated with sciatica can be severe, most cases resolve with non-operative treatments in a few weeks. People who have severe sciatica that’s associated with significant leg weakness or bowel or bladder changes might be candidates for surgery.
Symptoms
Pain that radiates from your lower (lumbar) spine to your buttock and down the back of your leg is the hallmark of sciatica. You might feel the discomfort almost anywhere along the nerve pathway, but it’s especially likely to follow a path from your low back to your buttock and the back of your thigh and calf.
The pain can vary widely, from a mild ache to a sharp, burning sensation or excruciating pain. Sometimes it can feel like a jolt or electric shock. It can be worse when you cough or sneeze, and prolonged sitting can aggravate symptoms. Usually only one side of your body is affected.
Some people also have numbness, tingling or muscle weakness in the affected leg or foot. You might have pain in one part of your leg and numbness in another part.
When to see a doctor
Mild sciatica usually goes away over time. Call your doctor if self-care measures fail to ease your symptoms or if your pain lasts longer than a week, is severe or becomes progressively worse. Get immediate medical care if:
- You have sudden, severe pain in your low back or leg and numbness or muscle weakness in your leg
- The pain follows a violent injury, such as a traffic accident
- You have trouble controlling your bowels or bladder
Causes
Sciatica occurs when the sciatic nerve becomes pinched, usually by a herniated disk in your spine or by an overgrowth of bone (bone spur) on your vertebrae. More rarely, the nerve can be compressed by a tumor or damaged by a disease such as diabetes.
Risk factors
Risk factors for sciatica include:
- Age. Age-related changes in the spine, such as herniated disks and bone spurs, are the most common causes of sciatica.
- Obesity. By increasing the stress on your spine, excess body weight can contribute to the spinal changes that trigger sciatica.
- Occupation. A job that requires you to twist your back, carry heavy loads or drive a motor vehicle for long periods might play a role in sciatica, but there’s no conclusive evidence of this link.
- Prolonged sitting. People who sit for prolonged periods or have a sedentary lifestyle are more likely to develop sciatica than active people are.
- Diabetes. This condition, which affects the way your body uses blood sugar, increases your risk of nerve damage.
Complications
Although most people recover fully from sciatica, often without treatment, sciatica can potentially cause permanent nerve damage. Seek immediate medical attention if you have:
- Loss of feeling in the affected leg
- Weakness in the affected leg
- Loss of bowel or bladder function
Prevention
It’s not always possible to prevent sciatica, and the condition may recur. The following can play a key role in protecting your back:
- Exercise regularly. To keep your back strong, pay special attention to your core muscles — the muscles in your abdomen and lower back that are essential for proper posture and alignment. Ask your doctor to recommend specific activities.
- Maintain proper posture when you sit. Choose a seat with good lower back support, armrests and a swivel base. Consider placing a pillow or rolled towel in the small of your back to maintain its normal curve. Keep your knees and hips level.
- Use good body mechanics. If you stand for long periods, rest one foot on a stool or small box from time to time. When you lift something heavy, let your lower extremities do the work. Move straight up and down. Keep your back straight and bend only at the knees. Hold the load close to your body. Avoid lifting and twisting simultaneously. Find a lifting partner if the object is heavy or awkward.
BY [ Mayo Clinic Staff]